Bootstrap Modal Button
Overview
Occasionally we really need to set the attention on a special info leaving every thing others dimmed behind making confident we have definitely obtained the website visitor's concentration or perhaps have tons of details needed to be obtainable through the page yet so extensive it surely might bore and push back the people browsing the web page.
For these sorts of circumstances the modal component is pretty much valuable. What exactly it executes is representing a dialog box operating a vast area of the monitor diming out anything other things.
The Bootstrap 4 framework has everything needed to have for producing this type of feature using least efforts and a practical direct construction.
Bootstrap Modal is structured, however, flexible dialog assists powered via JavaScript. They assist a lot of use cases from user alert to truly custom made web content and come with a handful of practical subcomponents, sizings, and even more.
Tips about how Bootstrap Modal Popup works
Just before getting started having Bootstrap's modal element, make sure to read the following considering that Bootstrap menu options have already reformed.
- Modals are created with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. They are actually located over everything else in the document and remove scroll from the
<body>- Selecting the modal "backdrop" is going to automatically finalize the modal.
- Bootstrap basically holds a single modal window at once. Embedded modals usually are not maintained while we think them to remain poor user experiences.
- Modals application
position:fixeda.modal- One again , due to
position: fixed- And finally, the
autofocusKeep reading for demos and application tips.
- Because of how HTML5 specifies its semantics, the autofocus HTML attribute provides no result in Bootstrap modals. To reach the exact same result, work with some custom-made JavaScript:
$('#myModal').on('shown.bs.modal', function ()
$('#myInput').focus()
)To start off we need to have a switch on-- an anchor or switch to be clicked on so the modal to become displayed. To achieve in this way just assign
data-toggle=" modal"data-target="#myModal-ID"Instruction
Now why don't we produce the Bootstrap Modal in itself-- in the first place we need to have a wrap element containing the entire aspect-- specify it
.modalA smart idea would certainly be as well incorporating the
.fadeIf those two don't match the trigger won't actually fire the modal up, you would also want to add the same ID which you have defined in the modal trigger since otherwise.
As soon as that has been completed we desire an special element possessing the actual modal content-- specify the
.modal-dialog.modal-sm.modal-lg.modal-content.modal-header.modal-bodyOptionally you might actually want to incorporate a close button inside the header appointing it the class
.closedata-dismiss="modal"Pretty much this id the structure the modal parts have within the Bootstrap framework and it really has stayed the equivalent in both Bootstrap version 3 and 4. The brand-new version comes with a number of new solutions but it seems that the dev crew assumed the modals do the job all right the manner they are in this way they directed their attention off them so far.
Right now, lets have a look at the several forms of modals and their code.
Modal elements
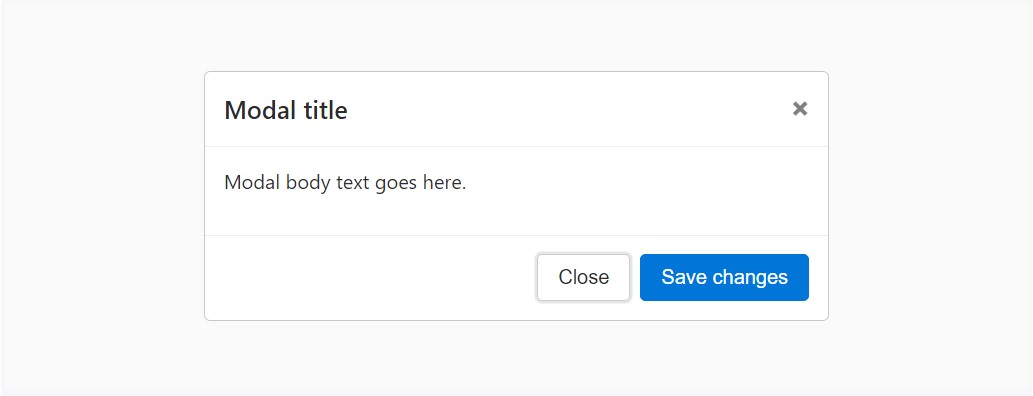
Listed here is a static modal sample ( suggesting its
positiondisplaypadding<div class="modal fade">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<p>Modal body text goes here.</p>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Live demo
Whenever you are going to employ a code listed here - a functioning modal test will be triggered as showned on the image. It will definitely go down and fade in from the high point of the page.
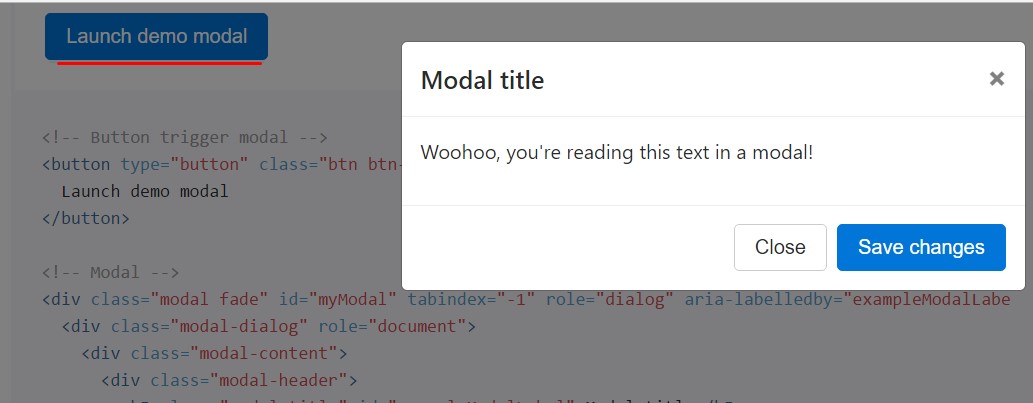
<!-- Button trigger modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal">
Launch demo modal
</button>
<!-- Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="myModal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLabel">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
...
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Scrolling extensive web content
They scroll independent of the page itself when modals become too long for the user's viewport or device. Work the demo listed here to notice precisely what we point to ( find more).
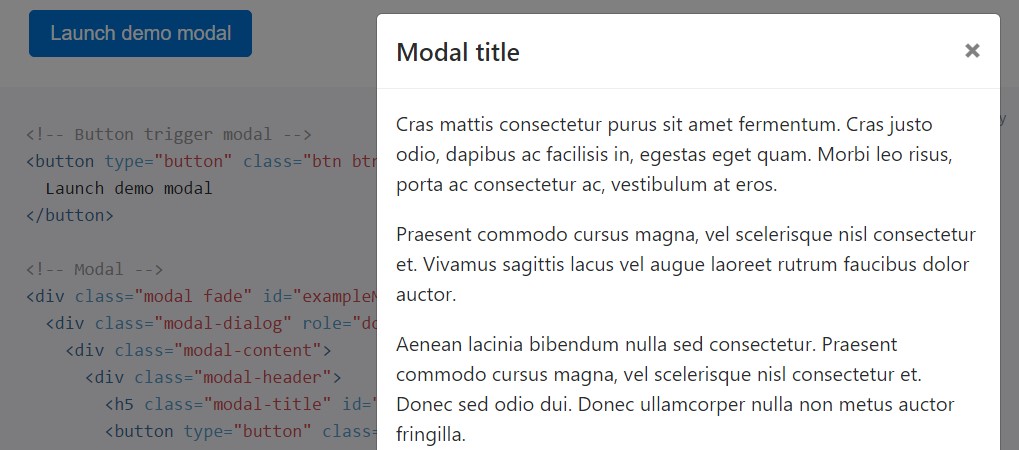
<!-- Button trigger modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModalLong">
Launch demo modal
</button>
<!-- Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="exampleModalLong" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLongTitle" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLongTitle">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
...
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Tooltips plus popovers
Tooltips plus popovers are able to be placed inside modals as demanded. Any tooltips and popovers within are also automatically dismissed when modals are closed.
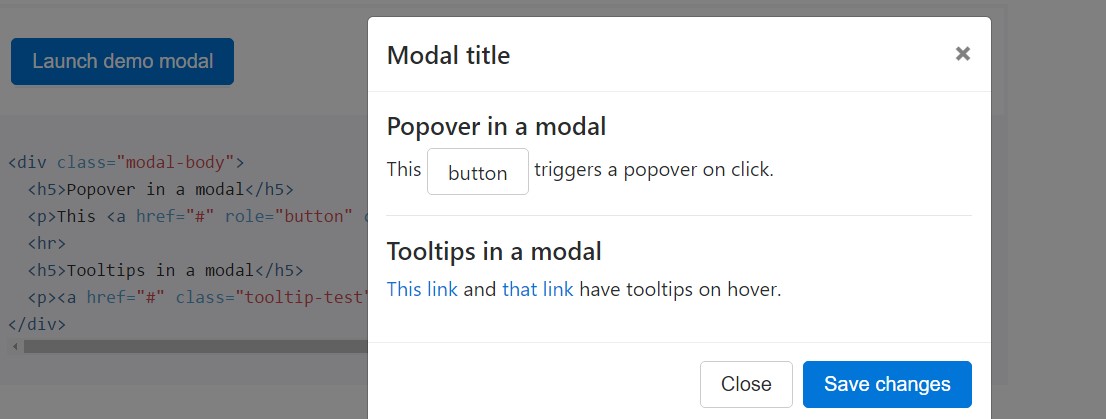
<div class="modal-body">
<h5>Popover in a modal</h5>
<p>This <a href="#" role="button" class="btn btn-secondary popover-test" title="Popover title" data-content="Popover body content is set in this attribute.">button</a> triggers a popover on click.</p>
<hr>
<h5>Tooltips in a modal</h5>
<p><a href="#" class="tooltip-test" title="Tooltip">This link</a> and <a href="#" class="tooltip-test" title="Tooltip">that link</a> have tooltips on hover.</p>
</div>Making use of the grid
Incorporate the Bootstrap grid system inside a modal by simply nesting
.container-fluid.modal-body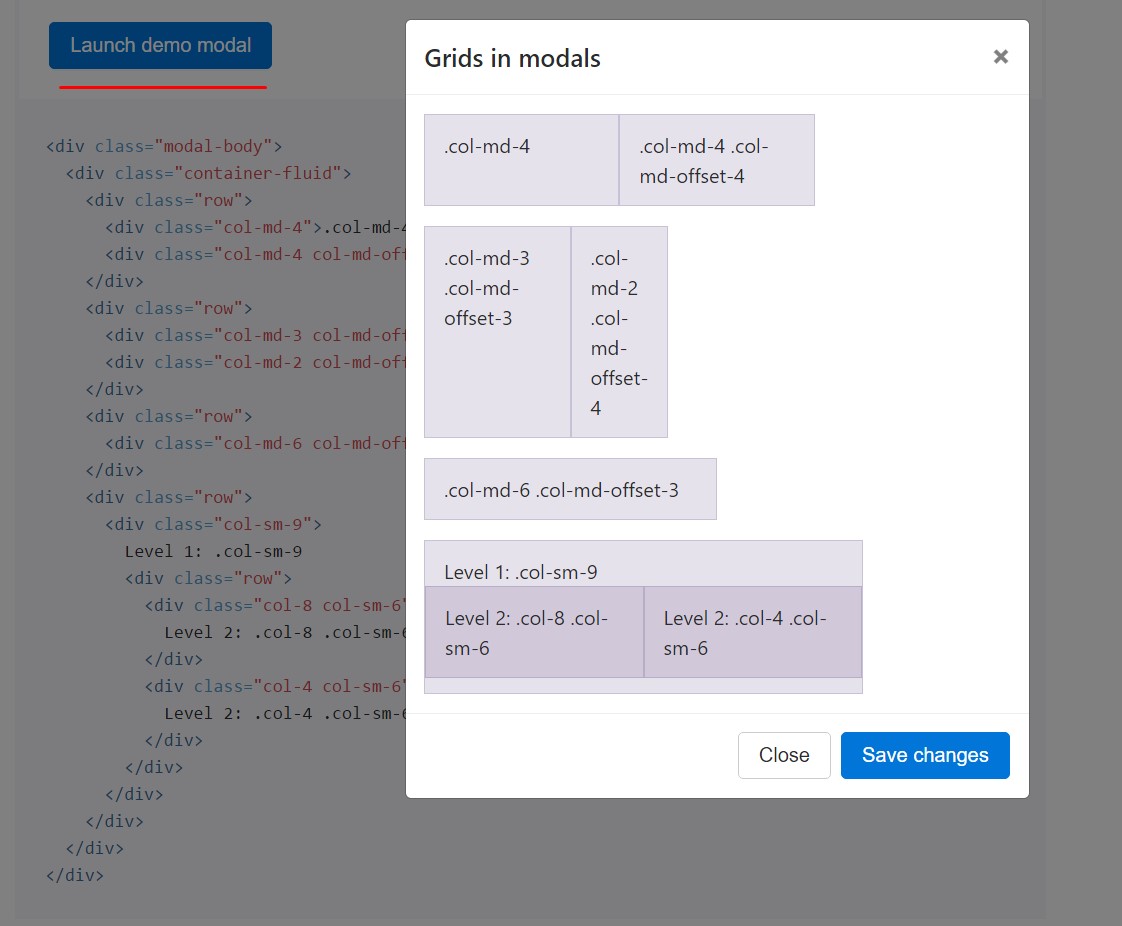
<div class="modal-body">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-md-4 col-md-offset-4">.col-md-4 .col-md-offset-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3 col-md-offset-3">.col-md-3 .col-md-offset-3</div>
<div class="col-md-2 col-md-offset-4">.col-md-2 .col-md-offset-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 col-md-offset-3">.col-md-6 .col-md-offset-3</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-9">
Level 1: .col-sm-9
<div class="row">
<div class="col-8 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-8 .col-sm-6
</div>
<div class="col-4 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-4 .col-sm-6
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Varying modal web content
Use a number of tabs that all cause the identical modal using a little bit different materials? Employ
event.relatedTargetdata-*Listed here is a live demo complied with by example HTML and JavaScript. For additional information, check out the modal events files with regard to details on
relatedTarget
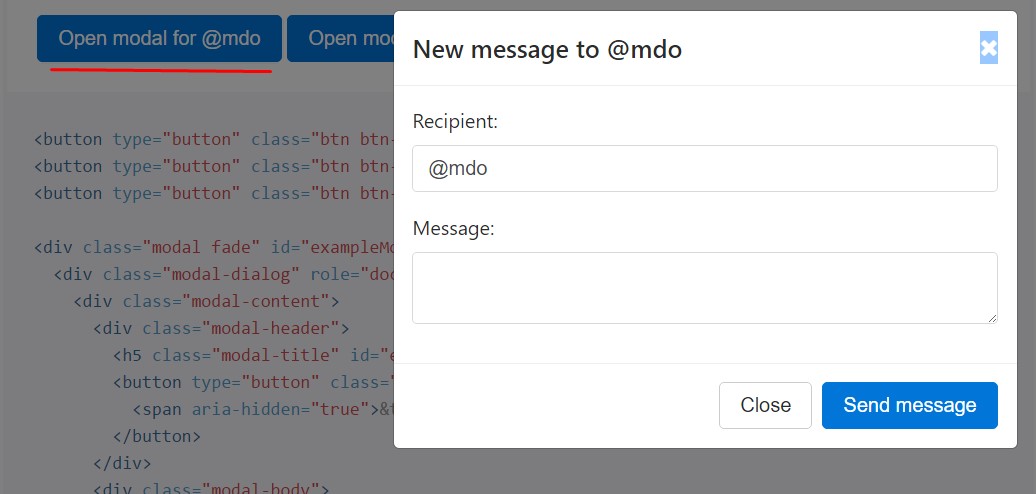
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@mdo">Open modal for @mdo</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@fat">Open modal for @fat</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@getbootstrap">Open modal for @getbootstrap</button>
<div class="modal fade" id="exampleModal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLabel">New message</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="recipient-name" class="form-control-label">Recipient:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="recipient-name">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="message-text" class="form-control-label">Message:</label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="message-text"></textarea>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Send message</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>$('#exampleModal').on('show.bs.modal', function (event)
var button = $(event.relatedTarget) // Button that triggered the modal
var recipient = button.data('whatever') // Extract info from data-* attributes
// If necessary, you could initiate an AJAX request here (and then do the updating in a callback).
// Update the modal's content. We'll use jQuery here, but you could use a data binding library or other methods instead.
var modal = $(this)
modal.find('.modal-title').text('New message to ' + recipient)
modal.find('.modal-body input').val(recipient)
)Get rid of animation
For modals which just simply appear rather than fade in to view, remove the
.fade<div class="modal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="..." aria-hidden="true">
...
</div>Lively levels
On the occasion that the height of a modal switch even though it is open, you need to call
$(' #myModal'). data(' bs.modal'). handleUpdate()Ease of access
Adding YouTube videos
Implanting YouTube videos clips in modals needs added JavaScript not within Bootstrap to instantly end playback and more.
Alternative sizings
Modals possess two optional proportions, provided via modifier classes to get put on a
.modal-dialog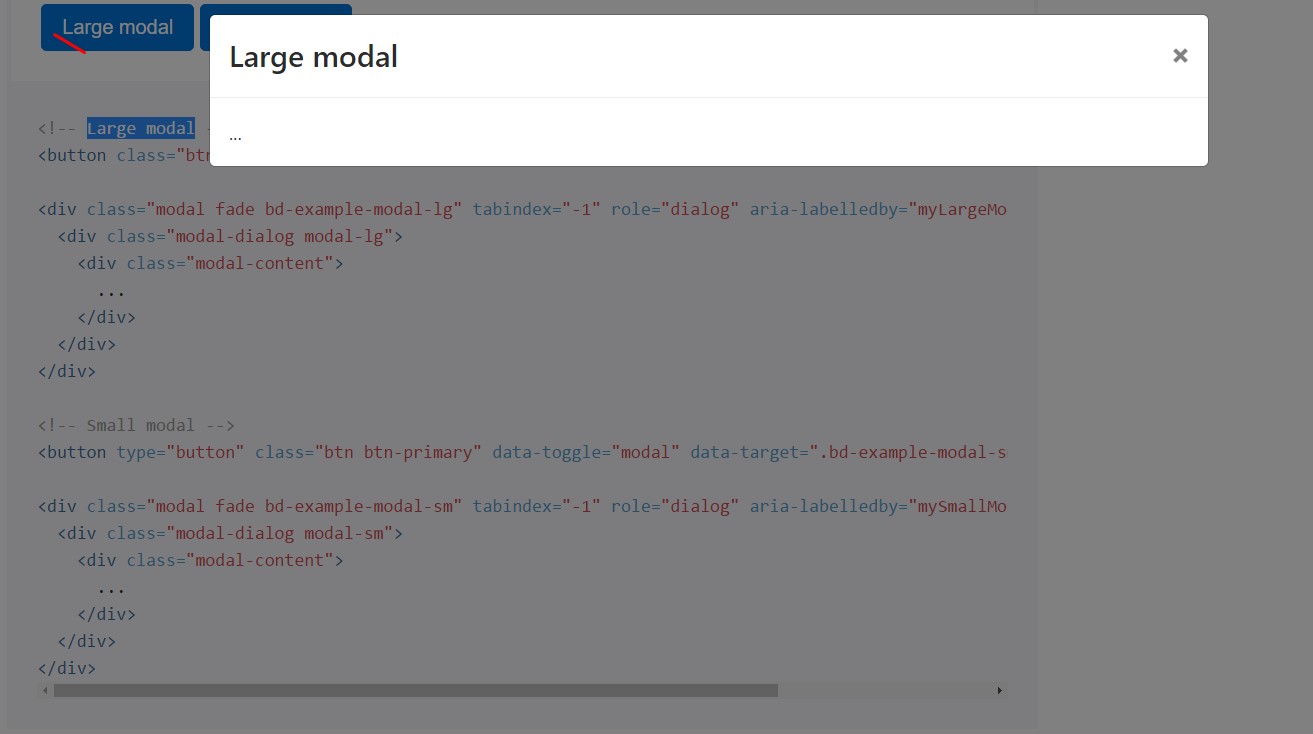
<!-- Large modal -->
<button class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target=".bd-example-modal-lg">Large modal</button>
<div class="modal fade bd-example-modal-lg" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="myLargeModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog modal-lg">
<div class="modal-content">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>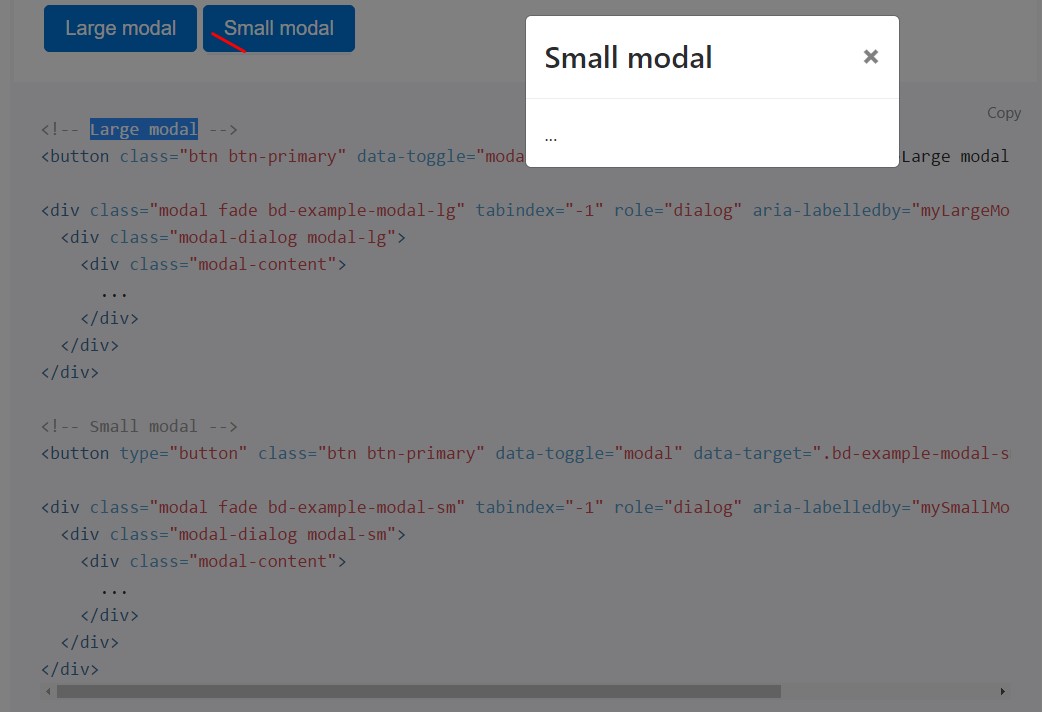
<!-- Small modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target=".bd-example-modal-sm">Small modal</button>
<div class="modal fade bd-example-modal-sm" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="mySmallModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog modal-sm">
<div class="modal-content">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>Usage
The modal plugin toggles your hidden content on demand, via data attributes or JavaScript.
Via information attributes
Turn on a modal without writing JavaScript. Put
data-toggle="modal"data-target="#foo"href="#foo"<button type="button" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#myModal">Launch modal</button>Via JavaScript
Call a modal with id
myModal$('#myModal'). modal( options).Options
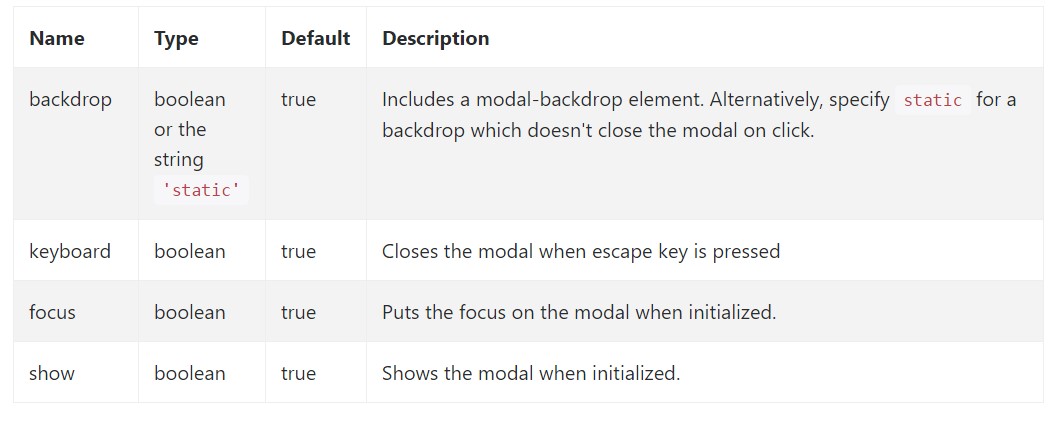
Options may possibly be passed through details attributes or JavaScript. For information attributes, add the option name to
data-data-backdrop=""Check also the image below:
Methods
.modal(options)
.modal(options)Switches on your web content as a modal. Approves an optional options
object$('#myModal').modal(
keyboard: false
).modal('toggle')
.modal('toggle')Manually toggles a modal. Returns to the user just before the modal has in fact been displayed or covered (i.e. just before the
shown.bs.modalhidden.bs.modal$('#myModal').modal('toggle').modal('show')
.modal('show')Manually starts a modal. Go back to the caller just before the modal has really been revealed (i.e. before the
shown.bs.modal$('#myModal').modal('show').modal('hide')
.modal('hide')Manually covers a modal. Go back to the caller before the modal has actually been concealed (i.e. before the
hidden.bs.modal$('#myModal').modal('hide')Bootstrap modals events
Bootstrap's modal class exposes a number of events for entraping in to modal functionality. All modal events are fired at the modal in itself (i.e. at the
<div class="modal">
$('#myModal').on('hidden.bs.modal', function (e)
// do something...
)Final thoughts
We saw precisely how the modal is made yet exactly what would probably be in it?
The answer is-- practically anything-- coming from a extensive titles and aspects plain part with a few headings to the most complex construction which using the modifying design approaches of the Bootstrap framework might really be a page within the webpage-- it is technically achievable and the option of implementing it is up to you.
Do have in head however if ever at a specific point the content to be soaked the modal becomes far excessive perhaps the more effective method would be applying the entire element into a separate web page if you want to gain quite greater appearance and utilization of the whole screen size provided-- modals a suggested for small blocks of material urging for the viewer's treatment .
Look at a few on-line video tutorials about Bootstrap modals:
Connected topics:
Bootstrap modals: formal information

W3schools:Bootstrap modal information
Bootstrap 4 with remote modal