Bootstrap Form Example
Introduction
Bootstrap offers several form regulation looks, layout options, and custom made components for producing a variety of Bootstrap Form Inline.
Forms offer the great resolution for getting several suggestions from the website visitors of our webpages. In case that it is definitely a straightforward connection or possibly subscription form including simply a handful of areas or else a complicated and very well thought request the Bootstrap 4 platform got all things that is definitely required to do the function and obtain wonderful responsive appearance.
By default inside the Bootstrap framework the form elements are styled to span all size of its parent feature-- this stuff gets reached by appointing the
.form-control.form-groupBootstrap Form Elements commands
Bootstrap's form controls increase with regards to our Rebooted form appearances along with classes.
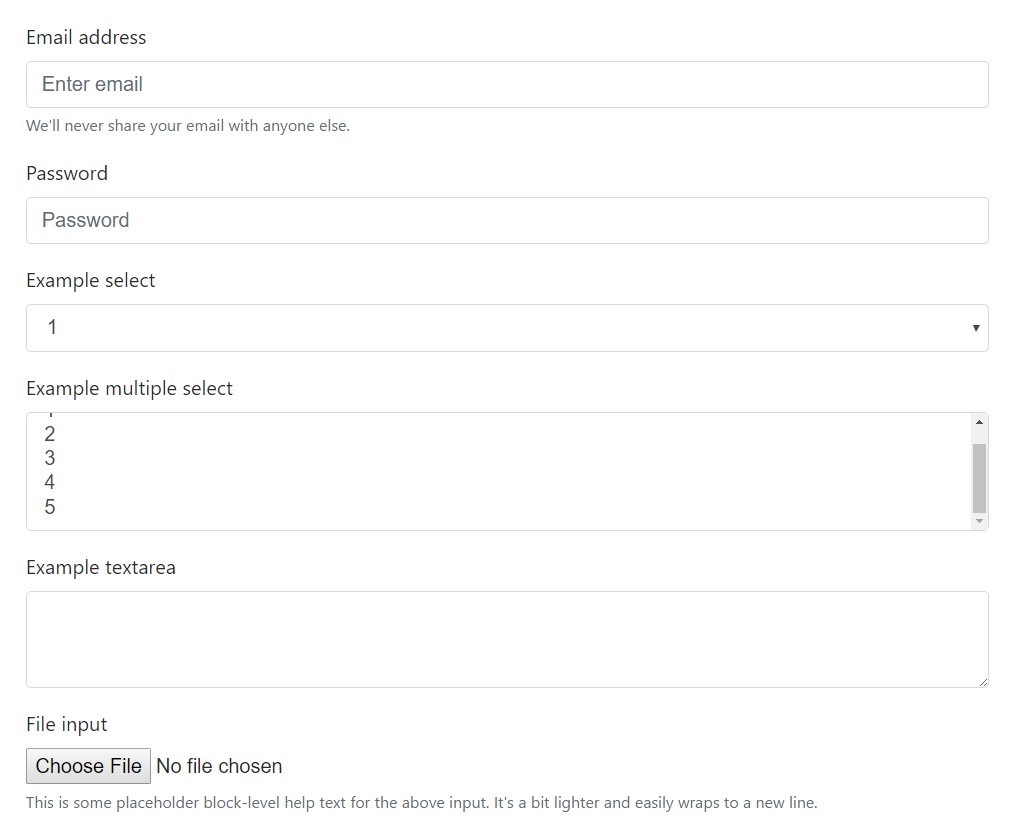
Make use of such classes to opt inside their customized screens to get a additional constant rendering across internet browsers and gadgets . The example form shown below shows usual HTML form components which get upgraded varieties directly from Bootstrap together with more classes.
Keep in mind, due to the fact that Bootstrap applies the HTML5 doctype, all inputs must come with a
type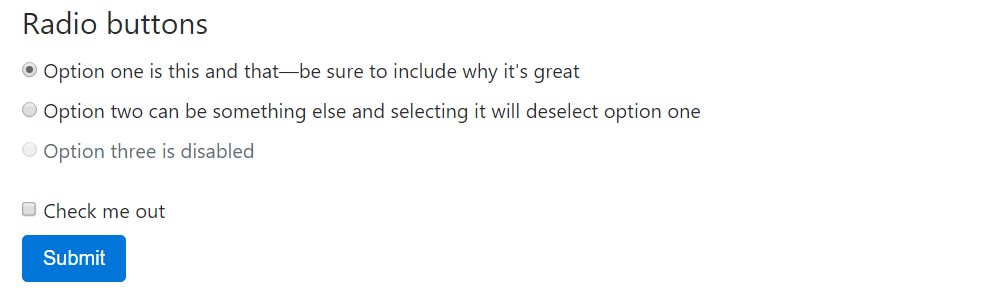
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">Email address</label>
<input type="email" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp" placeholder="Enter email">
<small id="emailHelp" class="form-text text-muted">We'll never share your email with anyone else.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1" placeholder="Password">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleSelect1">Example select</label>
<select class="form-control" id="exampleSelect1">
<option>1</option>
<option>2</option>
<option>3</option>
<option>4</option>
<option>5</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleSelect2">Example multiple select</label>
<select multiple class="form-control" id="exampleSelect2">
<option>1</option>
<option>2</option>
<option>3</option>
<option>4</option>
<option>5</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleTextarea">Example textarea</label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="exampleTextarea" rows="3"></textarea>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputFile">File input</label>
<input type="file" class="form-control-file" id="exampleInputFile" aria-describedby="fileHelp">
<small id="fileHelp" class="form-text text-muted">This is some placeholder block-level help text for the above input. It's a bit lighter and easily wraps to a new line.</small>
</div>
<fieldset class="form-group">
<legend>Radio buttons</legend>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>
</fieldset>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input">
Check me out
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
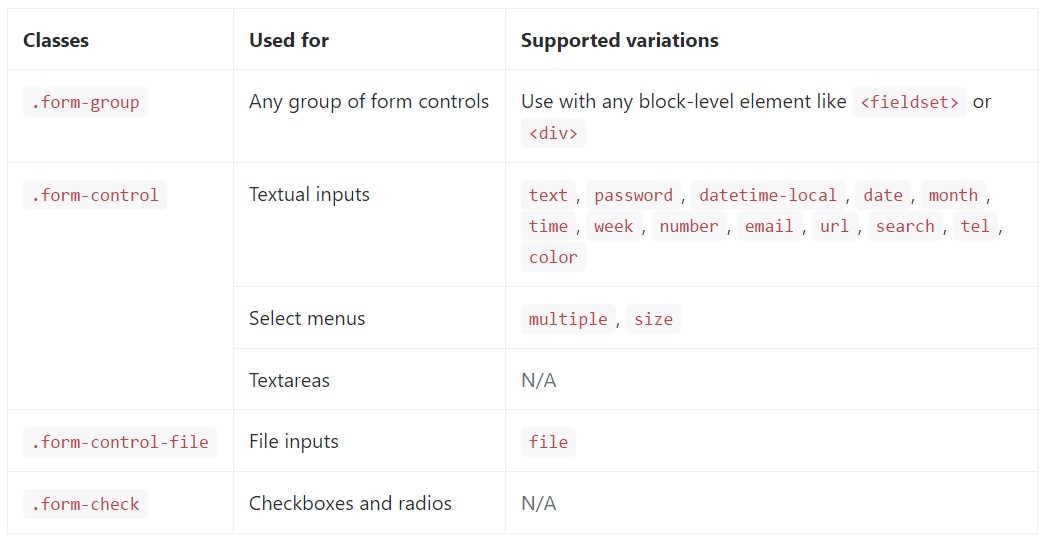
</form>Shown below is a full catalog of the certain Bootstrap Form Group regulations assisted by Bootstrap as well as the classes that customise them. Supplementary information is offered for each group.
Textual inputs
Listed below are the illustrations of
.form-control<input>type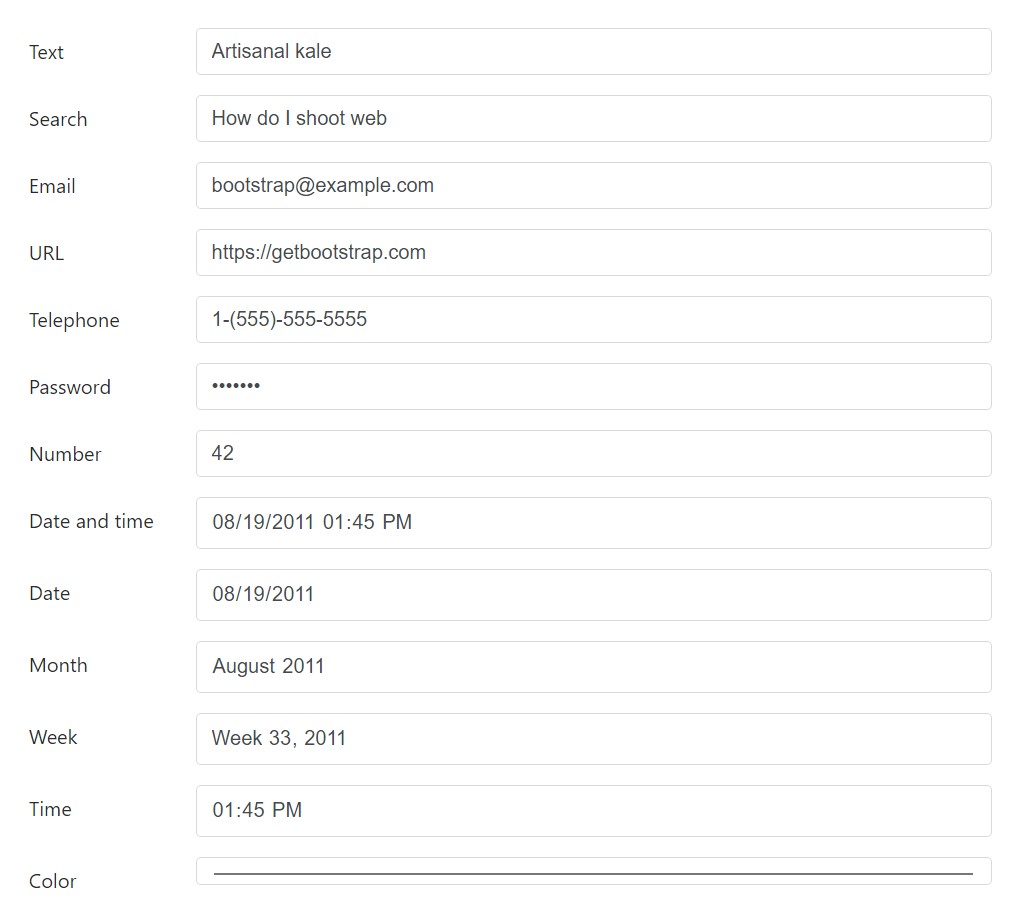
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-text-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Text</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="text" value="Artisanal kale" id="example-text-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-search-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Search</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="search" value="How do I shoot web" id="example-search-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-email-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="email" value="[email protected]" id="example-email-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-url-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">URL</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="url" value="https://getbootstrap.com" id="example-url-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-tel-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Telephone</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="tel" value="1-(555)-555-5555" id="example-tel-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-password-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="password" value="hunter2" id="example-password-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-number-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Number</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="number" value="42" id="example-number-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-datetime-local-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Date and time</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="datetime-local" value="2011-08-19T13:45:00" id="example-datetime-local-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-date-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Date</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="date" value="2011-08-19" id="example-date-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-month-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Month</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="month" value="2011-08" id="example-month-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-week-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Week</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="week" value="2011-W33" id="example-week-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-time-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Time</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="time" value="13:45:00" id="example-time-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-color-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Color</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="color" value="#563d7c" id="example-color-input">
</div>
</div>Form configurations
As Bootstrap uses
display: blockwidth :100%Form groups
The
.form-groupmargin-bottom<fieldset><div>
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="formGroupExampleInput">Example label</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="formGroupExampleInput" placeholder="Example input">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="formGroupExampleInput2">Another label</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="formGroupExampleInput2" placeholder="Another input">
</div>
</form>Inline forms
Use the
.form-inline- Controls are
display: flex- Controls and also input groups obtain
width: autowidth: 100%- Controls exclusively show up inline inside viewports that are at very least 576px big to consider thin viewports on mobile devices.
You may require to personally address the size and arrangement of individual form controls plus spacing utilities (as indicated here) Lastly, ensure to always feature a
<label>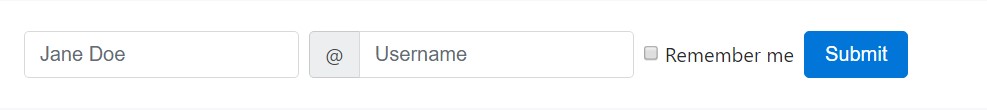
<form class="form-inline">
<label class="sr-only" for="inlineFormInput">Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0" id="inlineFormInput" placeholder="Jane Doe">
<label class="sr-only" for="inlineFormInputGroup">Username</label>
<div class="input-group mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<div class="input-group-addon">@</div>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="inlineFormInputGroup" placeholder="Username">
</div>
<div class="form-check mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox"> Remember me
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
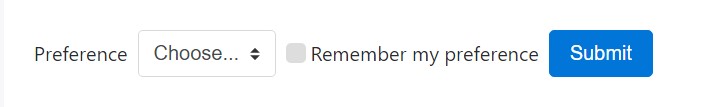
</form>Custom-made form controls also picks are likewise supported.
<form class="form-inline">
<label class="mr-sm-2" for="inlineFormCustomSelect">Preference</label>
<select class="custom-select mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0" id="inlineFormCustomSelect">
<option selected>Choose...</option>
<option value="1">One</option>
<option value="2">Two</option>
<option value="3">Three</option>
</select>
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Remember my preference</span>
</label>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>Alternatives to hidden labels
Assistive systems like screen readers will certainly have issue with your forms in case you do not provide a label for every single input. For these particular inline forms, you have the ability to cover the labels employing the
.sr-onlyaria-labelaria-labelledbytitleplaceholderplaceholderUtilizing the Grid
For extra organised form layouts which are additionally responsive, you can utilize Bootstrap's predefined grid classes or else mixins to make horizontal forms. Provide the
.row.col-*-*Be sure to add
.col-form-label<label><legend>.col-form-legend<label>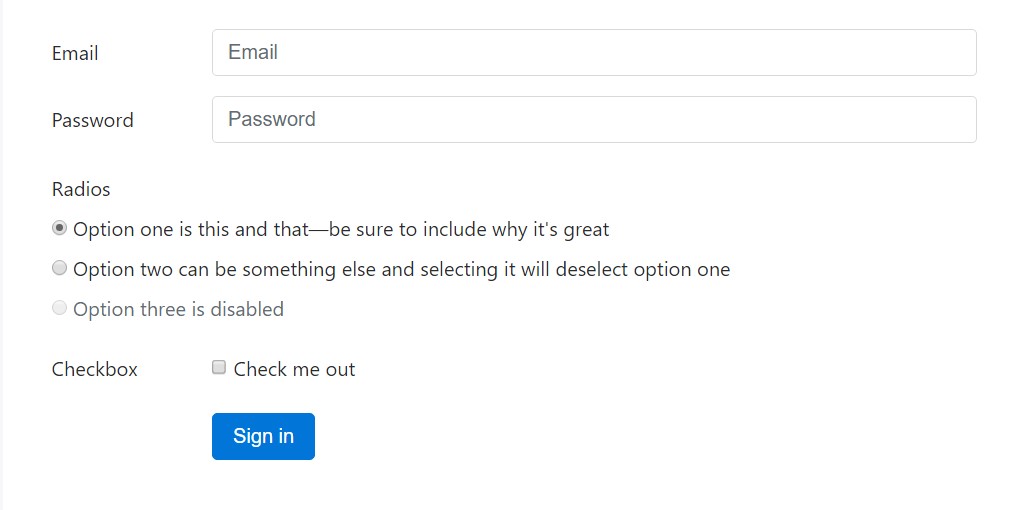
<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputEmail3" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control" id="inputEmail3" placeholder="Email">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputPassword3" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword3" placeholder="Password">
</div>
</div>
<fieldset class="form-group row">
<legend class="col-form-legend col-sm-2">Radios</legend>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>
</div>
</fieldset>
<div class="form-group row">
<label class="col-sm-2">Checkbox</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox"> Check me out
</label>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<div class="offset-sm-2 col-sm-10">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Sign in</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>Grid-based form designs additionally provide small and big inputs.
<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="lgFormGroupInput" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label col-form-label-lg">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-lg" id="lgFormGroupInput" placeholder="[email protected]">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="smFormGroupInput" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label col-form-label-sm">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-sm" id="smFormGroupInput" placeholder="[email protected]">
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>Checkboxes and radios
Default radios and checkboxes are greatly enhanced upon with the aid of
.form-checkThe disabled class will in addition light up the message coloration to help reveal the input's state.
Every checkbox and radio is wrapped within a
<label>- It supplies a larger hit areas for checking the control.
- It provides a useful and semantic wrapper in order to help us substitute the default
<input>- It produces the state of the
<input>We hide the default
<input>opacity.custom-control-indicator<input>contentWe apply the relative selector
~<input>: checked.custom-control-description<input>In the checked states, we use base64 embedded SVG icons from Open Iconic. This provides us the best control for styling and positioning across browsers and devices.
Checkboxes

<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>Customized checkboxes are able to also use the
: indeterminate
In case you are actually utilizing jQuery, something like this should do the trick:
$('.your-checkbox').prop('indeterminate', true)Radios

<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio1" name="radio" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio2" name="radio" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Or toggle this other custom radio</span>
</label>Default (stacked)
By default, any variety of checkboxes and radios that are really immediate relative will be vertically stacked as well as effectively spaced with
.form-check
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" value="">
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" value="" disabled>
Option two is disabled
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>Inline
Group checkboxes or else radios on the similar horizontal row simply by incorporating
.form-check-inline.form-check
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox1" value="option1"> 1
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox2" value="option2"> 2
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox3" value="option3" disabled> 3
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio1" value="option1"> 1
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio2" value="option2"> 2
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio3" value="option3" disabled> 3
</label>
</div>Without any labels
You really should not have a text message within the
<label>aria-label
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="blankCheckbox" value="option1" aria-label="...">
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="blankRadio" id="blankRadio1" value="option1" aria-label="...">
</label>
</div>Static controls
When you want to set plain text next to a form label inside a form, use the
.form-control-static
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<p class="form-control-static">[email protected]</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputPassword" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword" placeholder="Password">
</div>
</div>
</form>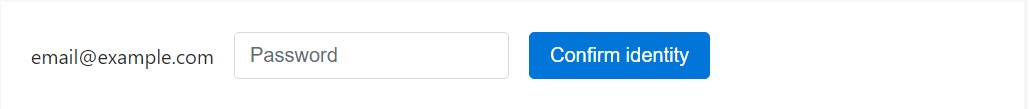
<form class="form-inline">
<div class="form-group">
<label class="sr-only">Email</label>
<p class="form-control-static">[email protected]</p>
</div>
<div class="form-group mx-sm-3">
<label for="inputPassword2" class="sr-only">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword2" placeholder="Password">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Confirm identity</button>
</form>Disabled status
Incorporate the
disablednot-allowed<input class="form-control" id="disabledInput" type="text" placeholder="Disabled input here..." disabled>Include the
disabled<fieldset>
<form>
<fieldset disabled>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="disabledTextInput">Disabled input</label>
<input type="text" id="disabledTextInput" class="form-control" placeholder="Disabled input">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="disabledSelect">Disabled select menu</label>
<select id="disabledSelect" class="form-control">
<option>Disabled select</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="checkbox">
<label>
<input type="checkbox"> Can't check this
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</fieldset>
</form> Caution relating to web link capabilities of <a>
<a>By default, web browsers will certainly treat all essential form controls (
<input><select><button><fieldset disabled><a ... class="btn btn-*">pointer-events: noneCross-browser consonance
As long as Bootstrap will apply these types of styles in all of the internet browsers, Internet Explorer 11 and below do not entirely assist the
disabled<fieldset>Readonly inputs
Provide the
readonly
<input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Readonly input here…" readonly>Control proportions
Determine heights applying classes like
.form-control-lg.col-lg-*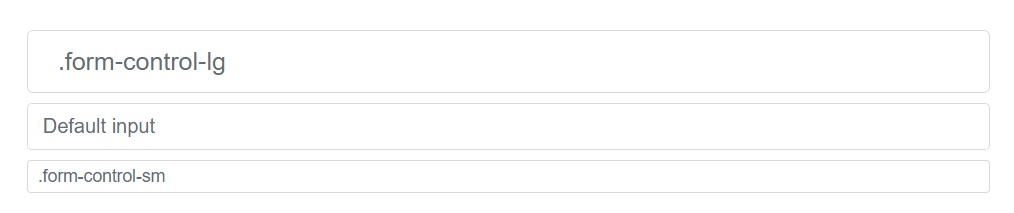
<input class="form-control form-control-lg" type="text" placeholder=".form-control-lg">
<input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Default input">
<input class="form-control form-control-sm" type="text" placeholder=".form-control-sm">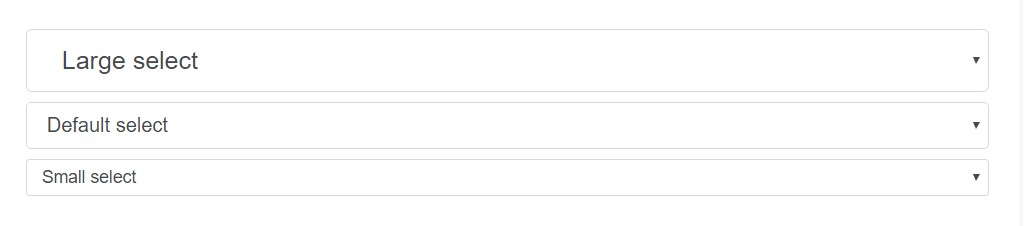
<select class="form-control form-control-lg">
<option>Large select</option>
</select>
<select class="form-control">
<option>Default select</option>
</select>
<select class="form-control form-control-sm">
<option>Small select</option>
</select>Column sizes
Wrap inputs within a grid columns, or any type of custom parent element, to easily enforce the wanted widths.
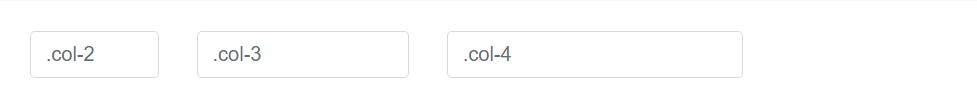
<div class="row">
<div class="col-2">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-2">
</div>
<div class="col-3">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-3">
</div>
<div class="col-4">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-4">
</div>
</div>Help content
The
.help-block.form-text.has-feedback.form-control-danger.form-control-warning.form-control-successAffiliating assistance message with form controls
Assistance text message ought to be explicitly associated with the form control it really connects to applying the
aria-describedbyBlock level
Block support content-- for below inputs or for extended lines of the assistance content-- can be simply achieved by using
.form-textdisplay: block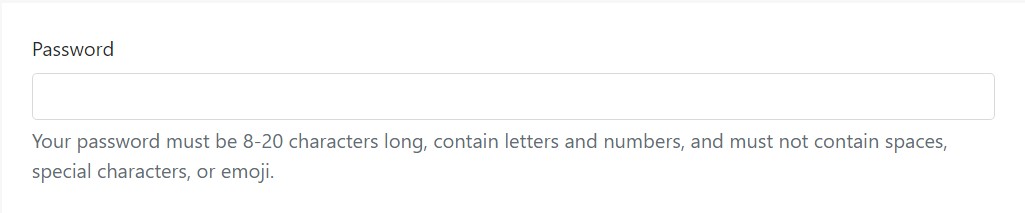
<label for="inputPassword5">Password</label>
<input type="password" id="inputPassword5" class="form-control" aria-describedby="passwordHelpBlock">
<p id="passwordHelpBlock" class="form-text text-muted">
Your password must be 8-20 characters long, contain letters and numbers, and must not contain spaces, special characters, or emoji.
</p>Inline
Inline words can employ any type of basic inline HTML element (be it a 'small', 'span', or else another).
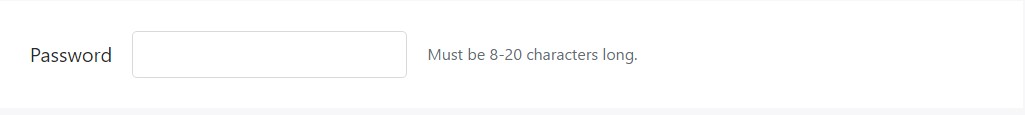
<form class="form-inline">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputPassword4">Password</label>
<input type="password" id="inputPassword4" class="form-control mx-sm-3" aria-describedby="passwordHelpInline">
<small id="passwordHelpInline" class="text-muted">
Must be 8-20 characters long.
</small>
</div>
</form>Validation
Bootstrap provides validation designs for danger, success, and warning states on the majority of form controls.
Ways to put to use
Here's a briefing of how they work:
- To use, put in
.has-warning.has-danger.has-success.col-form-label.form-control- Contextual validation text message, alongside your common form field support content, can possibly be added together with the utilization of
.form-control-feedback.has-*margincolor- Validation icons are
url()background-image- You may utilize your special base64 PNGs or perhaps SVGs via improving the Sass variables as well as recompiling.
- Icons are able to likewise be disabled absolutely through setting up the variables to
noneDefining conditions
Generally speaking, you'll need to employ a particular state for particular sorts of responses:
- Danger is ideal for when there's a blocking or required field. A user must fill this particular field properly to provide the form.
- Warning performs successfully for input values that are in progression, just like parole strength, or soft validation prior to a user tries to submit a form.
- And finally, success is optimal for conditions as you have per-field validation through a form and also desire to urge a user through the rest of the fields.
For instances
Here are some good examples of the previously mentioned classes at work. First off is your standard left-aligned fields together with labels, guidance content, and validation messaging.

<div class="form-group has-success">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputSuccess1">Input with success</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-success" id="inputSuccess1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Success! You've done it.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-warning">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputWarning1">Input with warning</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-warning" id="inputWarning1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Shucks, check the formatting of that and try again.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-danger">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputDanger1">Input with danger</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-danger" id="inputDanger1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Sorry, that username's taken. Try another?</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>All those equal states may in addition be employed along with horizontal forms.

<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row has-success">
<label for="inputHorizontalSuccess" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-success" id="inputHorizontalSuccess" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Success! You've done it.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row has-warning">
<label for="inputHorizontalWarning" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-warning" id="inputHorizontalWarning" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Shucks, check the formatting of that and try again.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row has-danger">
<label for="inputHorizontalDnger" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-danger" id="inputHorizontalDnger" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Sorry, that username's taken. Try another?</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>Radios and checkboxes happen to be also supported.

<div class="form-check has-success">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxSuccess" value="option1">
Checkbox with success
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check has-warning">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxWarning" value="option1">
Checkbox with warning
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check has-danger">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxDanger" value="option1">
Checkbox with danger
</label>
</div>Customized forms
To get more customization as well as cross web browser steadiness, make use of Bootstrap entirely custom-made form features to change the browser defaults. They're developed on top of semantic and convenient markup, in this way they're concrete substitutes for any sort of default form control.
Disabled
Customized checkboxes and radios can also be disabled . Add the
disabled<input>
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input" disabled>
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio3" name="radioDisabled" type="radio" class="custom-control-input" disabled>
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>Validation forms
Include the other states to your customized forms together with Bootstrap validation classes.

<div class="form-group has-success">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-warning">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-danger mb-0">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>Stacked
Custom made checkboxes and radios are inline to start. Add in a parent with class
.custom-controls-stacked
<div class="custom-controls-stacked">
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radioStacked1" name="radio-stacked" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radioStacked2" name="radio-stacked" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Or toggle this other custom radio</span>
</label>
</div>Select menu
Customized
<select>.custom-select
<select class="custom-select">
<option selected>Open this select menu</option>
<option value="1">One</option>
<option value="2">Two</option>
<option value="3">Three</option>
</select>File browser
The file input is the highly great of the bunch and demand added JavaScript in the case that you would love to catch all of them up through functional Choose file ... and selected file name text.
<label class="custom-file">
<input type="file" id="file" class="custom-file-input">
<span class="custom-file-control"></span>
</label>Here’s how to operate:
- We wrap the
<input><label>- We cover the default file
<input>opacity- We utilize
: after- We use
:before- We announce a
height<input>In other words, it is simply an entirely custom made component, entirely generated using CSS.
Transposing or else customing the files
The
: lang()$ custom-file-textes$custom-file-text: (
placeholder: (
en: "Choose file...",
es: "Seleccionar archivo..."
),
button-label: (
en: "Browse",
es: "Navegar"
)
);You'll need to prepare the language of your file (or subtree thereof) correctly in order for the appropriate text to be revealed. This can be performed employing the lang attribute or else the Content-Language HTTP header, with various other options.
Final thoughts
Generally all of these are the brand-new capabilities to the form components added within current fourth edition of the Bootstrap framework. The overall perception is the classes got extra specific and natural for this reason-- much simpler to use and having the customized control elements we can surely now receive so much more foreseeable appeal of the features we include within the web pages we create. Right now all that is actually left for us is determine the proper data we would need from our potential users to complete.
The best way to utilize the Bootstrap forms:
Related topics:
Bootstrap forms main documentation
Bootstrap guide
Support for Bootstrap Forms